What exactly are the different forms of “hyaluronic acid,” and why do they matter? Is sodium hyaluronate the same as hyaluronic acid? While they sound similar, their roles in skincare versus injectable treatments differ vastly. The form of the ingredient determines its stability, depth of penetration, and longevity.
This article analyzes the three core forms: Hyaluronic Acid vs. Sodium Hyaluronate vs. Cross-linked Sodium Hyaluronate to help you make informed choices.
Table of Contents
ToggleHyaluronic Acid vs. Sodium Hyaluronate vs. Cross-linked Sodium Hyaluronate
To understand the market for dermal filler products, one must first distinguish between the chemical variations of this molecule. While “hyaluronic acid” is the catch-all term used in marketing, the specific chemical form dictates whether it is a fleeting moisturizer or a long-lasting structural implant.
The Distinctions:
- Sodium Hyaluronate: This is the stable salt form of hyaluronic acid. In its pure acid form, hyaluronic acid is unstable, poorly soluble in water, and degrades quickly under heat or varying pH levels. Sodium Hyaluronate, however, boasts excellent water solubility and a broad pH stability range. It is the standard for topical skincare and hydrating sodium hyaluronate injections (skin boosters), where it acts as a humectant.
- Cross-linked Sodium Hyaluronate: This is the powerhouse of the aesthetic industry. Through chemical engineering, individual polymer chains are covalently bonded to form a 3D viscoelastic hydrogel network. This cross-linked sodium hyaluronate structure resists enzymatic degradation, making it the core material for volumizing fillers used in contouring.
Feature | Sodium Hyaluronate | Cross-linked Sodium Hyaluronate |
Structure | Linear, free polymer chains. | 3D cross-linked hydrogel network. |
Stability | Degrades in days (rapid turnover). | Lasts months (3–18 months). |
Primary Use | Topical creams, Skin Boosters (Mesotherapy). | Dermal Fillers (Volumizing, Contouring). |
Function | Hydration, barrier repair, signaling. | Structural support, lifting, shape creation. |
Resistance | Low resistance to Hyaluronidase. | High resistance (physically protects chains). |
1. Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic Acid (also known as Hyaluronan) is a naturally occurring high-molecular-weight biological polymer found throughout the human body, specifically in the skin, joint synovial fluid, and the extracellular matrix (ECM). Chemically, it exists in a free acid form with a carboxyl group(-COOH).
- Characteristics: In its pure acid state, HA is unstable. It has poor water solubility and is highly susceptible to rapid degradation when exposed to heat or varying pH levels.
- Limitations: Due to its instability and difficulty in processing, pure “Hyaluronic Acid” is rarely used directly in commercial manufacturing. While the term is widely used in marketing as a catch-all, the actual ingredient inside the bottle is almost always its salt form, Sodium Hyaluronate.
2. Sodium Hyaluronate
Sodium Hyaluronate is the sodium salt form (-COONa+) of Hyaluronic Acid. It is the industry standard for both topical skincare and non-volumizing injectable treatments (such as skin boosters or “Shuiguang” injections).
- Key Advantages: unlike pure HA, Sodium Hyaluronate is highly water-soluble and chemically stable across a broad pH range (3.0–8.5). It resists oxidation and has a longer shelf life.
- Mechanism: It acts as a powerful humectant. High Molecular Weight (HMW) SH forms a breathable film on the skin’s surface to lock in moisture, while Low Molecular Weight (LMW) SH penetrates deeper to signal cell repair.
3. Cross-linked Sodium Hyaluronate
Cross-linked Sodium Hyaluronate is the result of advanced chemical engineering, transforming the liquid SH into a robust, viscoelastic hydrogel. This is the core material used in Jingjia Medical’s HAFILLER product line.
- The Science: Using a cross-linking agent (typically BDDE), the individual polymer chains of Sodium Hyaluronate are permanently bonded together to form a 3D network.
- Function: This “cross-linking” physically shields the molecule from the body’s natural enzymes (hyaluronidase), extending its lifespan from mere days to 6–18 months. It transforms the substance from a liquid moisturizer into a structural gel capable of lifting sagging tissue, contouring the chin and nose, and filling deep wrinkles.
Why is Cross-linking Technology Key to Longevity and Contouring?
The transition from a liquid moisturizer to a structural implant relies entirely on cross-linking technology. Imagine building a house: standard sodium hyaluronate gel is like loose sand—excellent for covering ground but unable to hold a shape. Cross-linked sodium hyaluronate is like concrete reinforced with steel bars. The cross-linking agent acts as the cement, binding the loose chains into a robust structure that withstands physical pressure and resists the body’s natural enzymes.
Without this technology, sodium hyaluronate injections would dissolve within days, providing no lasting contouring effect. The degree of cross-linking determines the gel’s hardness and duration, allowing for tailored solutions ranging from soft lip fillers to firm chin implants.
Jingjia Medical
High-quality cross-linking requires purity and precision. This is where Jingjia Medical excels. As a national high-tech enterprise, Jingjia Medical has mastered the extraction of injection-grade raw materials and advanced medical sodium hyaluronate cross-linking technology.
Jingjia Medical is one of the earliest manufacturers in China within this product category to obtain EU CE certification. Currently, they boast one of the widest ranges of applications and the most comprehensive product portfolios for medical sodium hyaluronate gel in China. With nearly 30 years of manufacturing experience and over a decade of ODM/OEM expertise, Jingjia Medical provides a robust supply chain system, serving as a reliable manufacturing base for dozens of international brands and producing over 70 types of cross-linked sodium hyaluronate products.
For inquiries about product collaboration, customized development, or OEM/ODM solutions, please feel free to contact Jingjia Medical for professional support.
What Else May Be Used in Dermal Fillers?
While we focus on using hyaluronic acid derivatives, it is vital to understand where they sit in the broader landscape of dermal filler products.
Common Filler Materials
Material | Key Characteristics | Duration | Reversibility |
Cross-linked Sodium Hyaluronate | Natural hydration, viscoelastic, smooth integration. | 6–18 Months | Yes (Dissolvable) |
Calcium Hydroxylapatite | Heavier, stimulates collagen, opaque (not for lips). | 12–18 Months | No |
Poly-L-lactic Acid (PLLA) | Bio-stimulator, gradual results over time. | 2+ Years | No |
PMMA (Polymethylmethacrylate) | Permanent microspheres, requires surgical precision. | Permanent | No |
The reason hyaluronic acid dominates the skin treatment market is its safety profile. Cross-linked sodium hyaluronate is unique because it is reversible. If a patient is unhappy with the result or a complication occurs, the filler can be dissolved immediately using Hyaluronidase. This safety profile makes it the preferred choice for both practitioners and patients compared to permanent or semi-permanent alternatives.
Jingjia Medical – HAFILLER: Precision and Purity
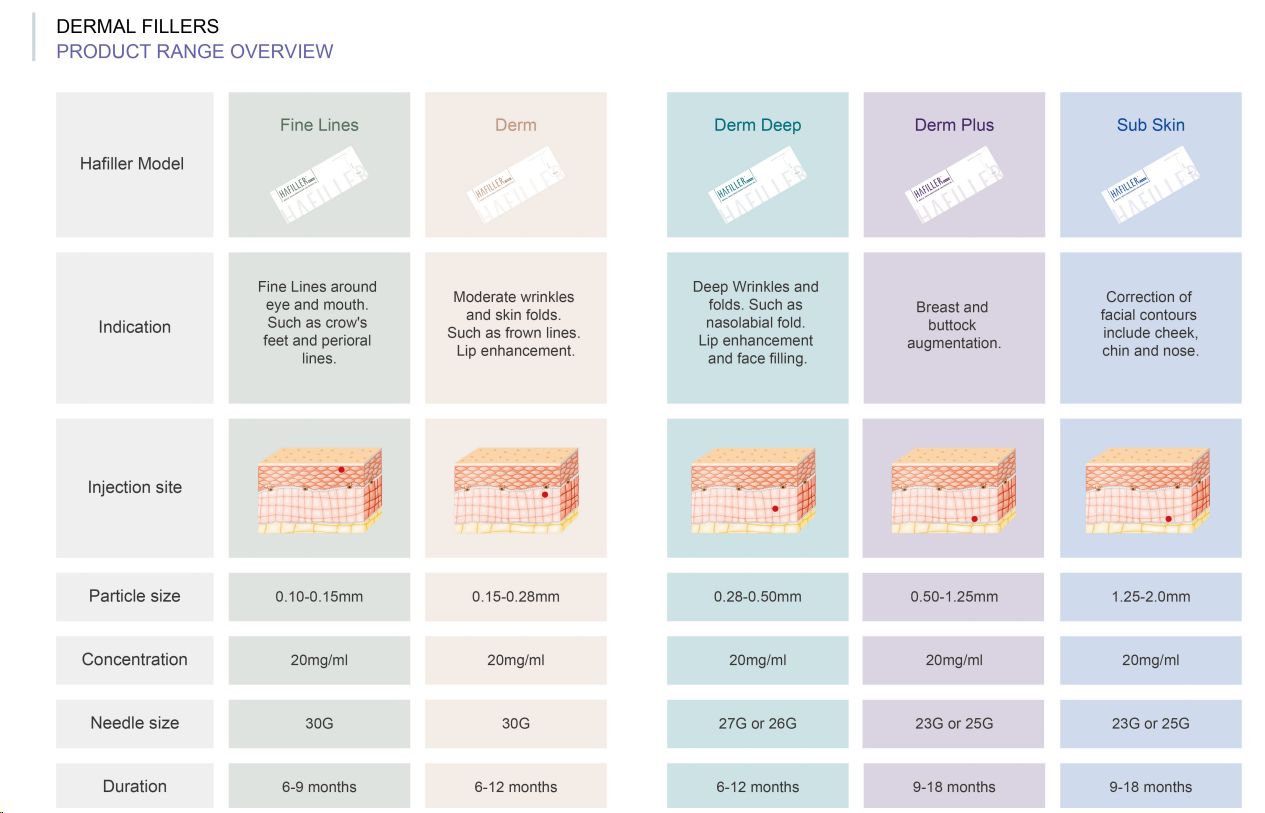
For global buyers seeking top-tier cross-linked sodium hyaluronate solutions, Jingjia Medical presents its proprietary brand, HAFILLER.
The HAFILLER product line offers a comprehensive range of options designed for different clinical indications:
Compliance and Manufacturing Excellence
Safety in injectables is non-negotiable. HAFILLER products are registered as Class III medical devices with the NMPA of China and hold European Union CE certification. The company operates under the ISO 13485 (2016) quality system and BSI MDSAP certification.
Jingjia Medical’s Manufacturing Standards:
- Purity: Utilizing medical-grade Water for Injection and over 30 purification processes, the purity of the Sodium Hyaluronate raw material reaches an impressive 95%~105%.
- Environment: Production occurs in a Class 100 sterile cleanroom (maximum 100 dust particles per cubic foot).
- Equipment: Key production equipment is imported from Europe, including the German OPTIMS filling machine and the Swedish GETINGE terminal sterilization cabinet. This ensures that every syringe of sodium hyaluronate gel meets the highest international safety standards.
Conclusion
Whether you are a distributor looking for a reliable ODM/OEM partner or a clinic seeking premium dermal filler products, quality manufacturing is paramount. Jingjia Medical combines advanced cross-linking technology with rigorous European-standard production to deliver safety and efficacy.
For inquiries about HAFILLER or manufacturing partnerships, contact Jingjia Medical today to ensure your supply chain is built on a foundation of purity and precision.
Main References:
[1] GUPTA R C, LALL R, SRIVASTAVA A, et al. Hyaluronic Acid: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Trajectory[J]. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 2019, 6: 192. DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00192.
[2] CHEN Jian-shu, WANG Jing-xi, YI Yu, GONG Hai-ping, YING Guo-qing. The Research Progress in Hyaluronic Acid[J]. China Biotechnology, 2015, 35(2): 111-118.